Medieval Europe Feudalism
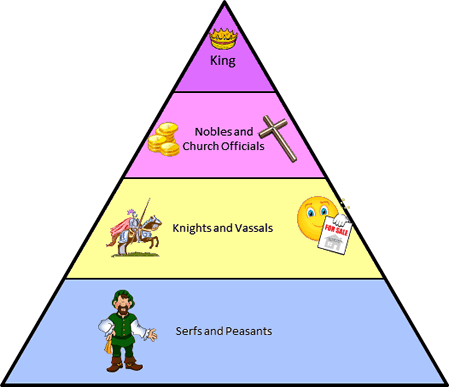
. /. /. Feudalism in Europe /Feudalism in EuropeFeudalism in Europe came into being during the 9th and 10th centuries. Feudalism in Europe image showing the Hierarchy of the Feudal system Feudalism DefinitionFeudalism refers to a set of military and legal obligations that shaped the society by basing the social hierarchy on land holdings.The status of different classes of society, under feudalism, was determined by the amount of land they owned.So for instance, peasants who didn’t own any land or simply lived on the land of the landowners were the lowest in the social strata.
Feudalism in Medieval Europe DRAFT. 75% average accuracy. Feudalism in Medieval Europe DRAFT. Europe During Medieval Times (TCI) 1.2k plays. Quiz not found! BACK TO EDMODO. Create a new quiz. Government Medieval Vocabulary. Feudalism: A political and economic system of Europe from the 9th to about the 15th century based on holding all land in fief or fee and the resulting relation of lord to vassal and characterized by homage, legal and military service of tenants, and forfeiture. Feudalism was the leading way of political and economic life in the Medieval era.
History of feudalism in EuropeFeudalism in Europe emerged somewhere around the 9th century and continued to exist as a dominant social structure until the 15th century. It began when mounted soldiers started establishing land holdings of their own, essentially a result of the decentralization of the power in the Empires.This lead to vast land holdings in the hands of these soldiers who eventually became the nobility and the land was further subdivided into vassals and fiefs.
PONY: FINISHING FIRST. The expertise of over 60 years in manufacturing professional finishing and pressing equipment, materializes in a complete range of state-of-the-art technological and reliable products able to satisfy the needs of all professionals in the industry. Find the product that best meets your requirements. View products catalogue. Pony minesweeper machine. Minesweeper A classic game of minesweeper! We designed it to match the specifications of the puzzle game that’s been entertaining folks for nearly three decades, complete with flags, customizable sizes, and more!
Feudalism arose in western Europe because?Feudalism in Western Europe arose in the area under the Frankish Empire during the 9th and 10th centuries. It arose because after Frankish armies and soldiers settled down, they were able to secure landholdings.Since previous social structures as were present during the Roman era had crumbled in Western Europe, feudalism emerged as a viable alternative for the new social circumstances. This is why it rapidly spread to other parts of Europe as well. Feudalism in EnglandFeudalism in England was brought to the country by William The Conqueror after his Norman invasion in the 11th century. After the invasion, William replaced the prevalent Anglo-Saxon aristocracy with a Norman-French nobility and this nobility began using feudal practices.After the conquest, William had claimed all of the land in England and then divided it between his own soldiers and barons.
In the feudal set-up, peasants were given land holdings which they could cultivate and live on in return of the provided labor to land-owners. Following the Black Death in the 14th century, feudalism began to decline in England. Image showing crown lands under the medieval feudal system History of Feudalism in FranceFeudalism in medieval Western Europe first emerged in France during the 9th and 10th century.
Originally the land was granted by the King to the nobles for their lifetime and the King could reclaim the land.However, over the years, the royal hold over the lands diminished and nobles began to hold land which was passed down as hereditary. This eventually led to greater power over their land, and greater independence, attained by the nobles and gave birth to feudalism.Feudalism in France was abolished in 17th century after the French Revolution. Abolition of Feudalism in FranceAfter the French Revolution in the 17th century, the National Constituent Assembly entirely abolished feudalism in France on August 4, 1789.The abolishment was directed both at the lands held by the nobility as well as the lands held by the Church. Lollipop chainsaw swan x reader.
With the abolishment of feudalism, all the feudal privileges of the nobility were also revoked. Feudalism in GermanyThe feudal system in Germany comprised of the King granting land to the upper vassals.
These upper vassals, in turn, granted land to the lower vassals. Lower vassals used bonded peasants to cultivate the land.Between each tier, loyalty and help during war was the price that had to be paid in return for the grant of land. Were also able to hold fiefs, although they didn’t have any land grants. In the Roman patronage system, a rich and influential patron essentially protected his clients in all aspects.In return, the clients accompanied and aided the patron in the war and other aspects. In Germanic kingdoms, all land belonged to the king who the distributed portions of it among his faithful nobles.

These influences eventually gave birth to proper feudalism in Germany under the Carolingian Kings. Decline of Feudalism in EuropeThe bedrock of feudalism was the need for the King to get armed help from nobles in return for land. A medieval Tithe Barn used to store one-tenth of the produce of peasants and Serfs End of feudalism in EuropeThe decline of feudalism was happening all over Europe by the 14th century. By the beginning of the 16th century, feudalism had already ended in most parts of the Europe.However, it remained in France where the 18th century French Revolution put a final end to it. Similarly, in Russia feudalism went on well until the mid-19th century when serfdom was finally abolished and marked an end to Russian feudalism.The end of feudalism in most parts of Europe was also an effect of the Renaissance and the consequent Industrial Revolution which increased demand for waged labor.